Bodor Tech Blog
Trending and helpful laser knowledge for your success
Laser Welding vs. TIG Welding - How is Laser Welding More Comprehensive?
Understanding the differences between laser welding and gas metal arc welding like TIG is crucial, as inappropriate technique could cause errors and delay working progress. The objective of this blog is providing everything you need to know about welding methods for making an informed decision when it comes to your welding projects.
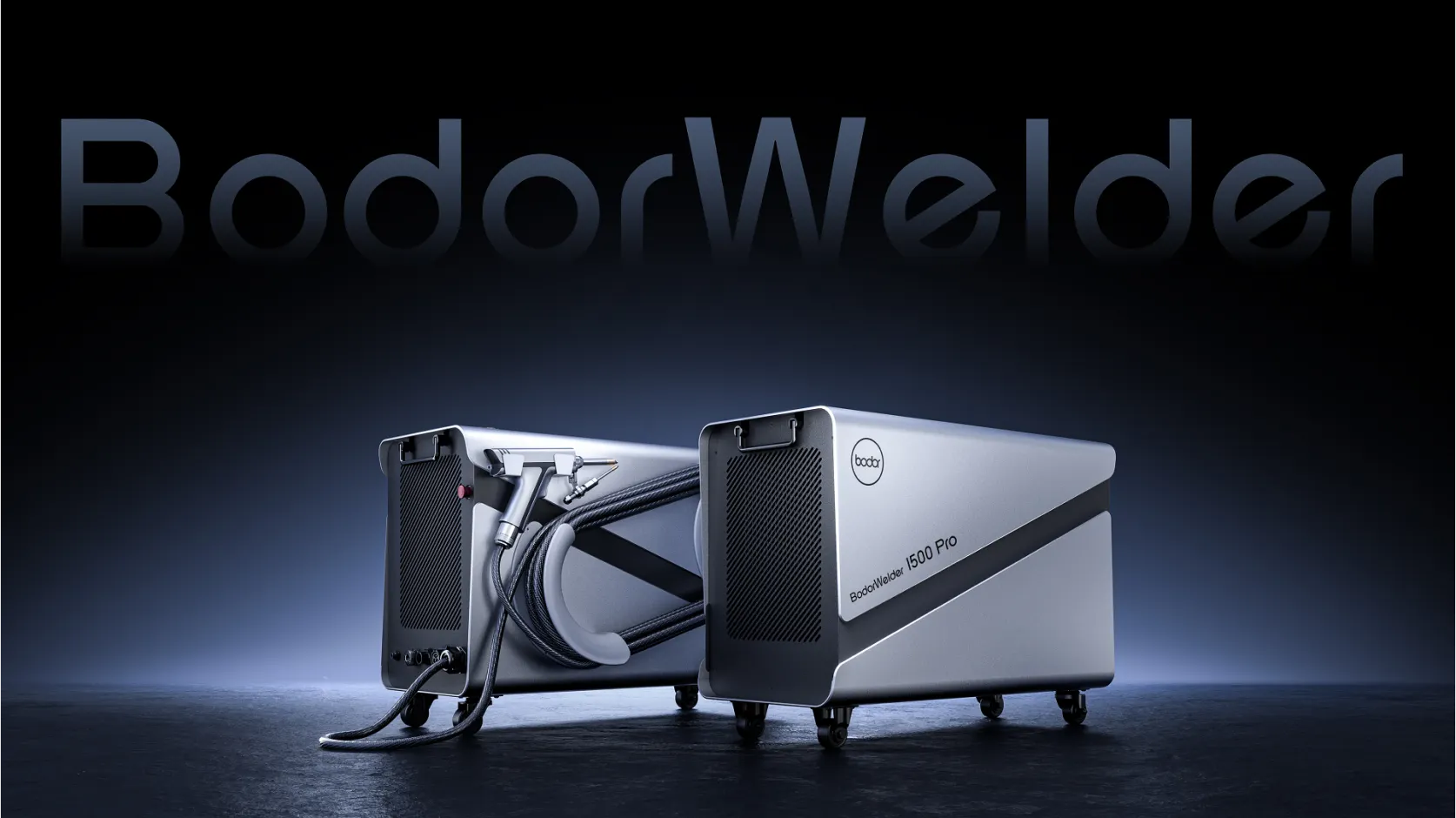

Laser welding
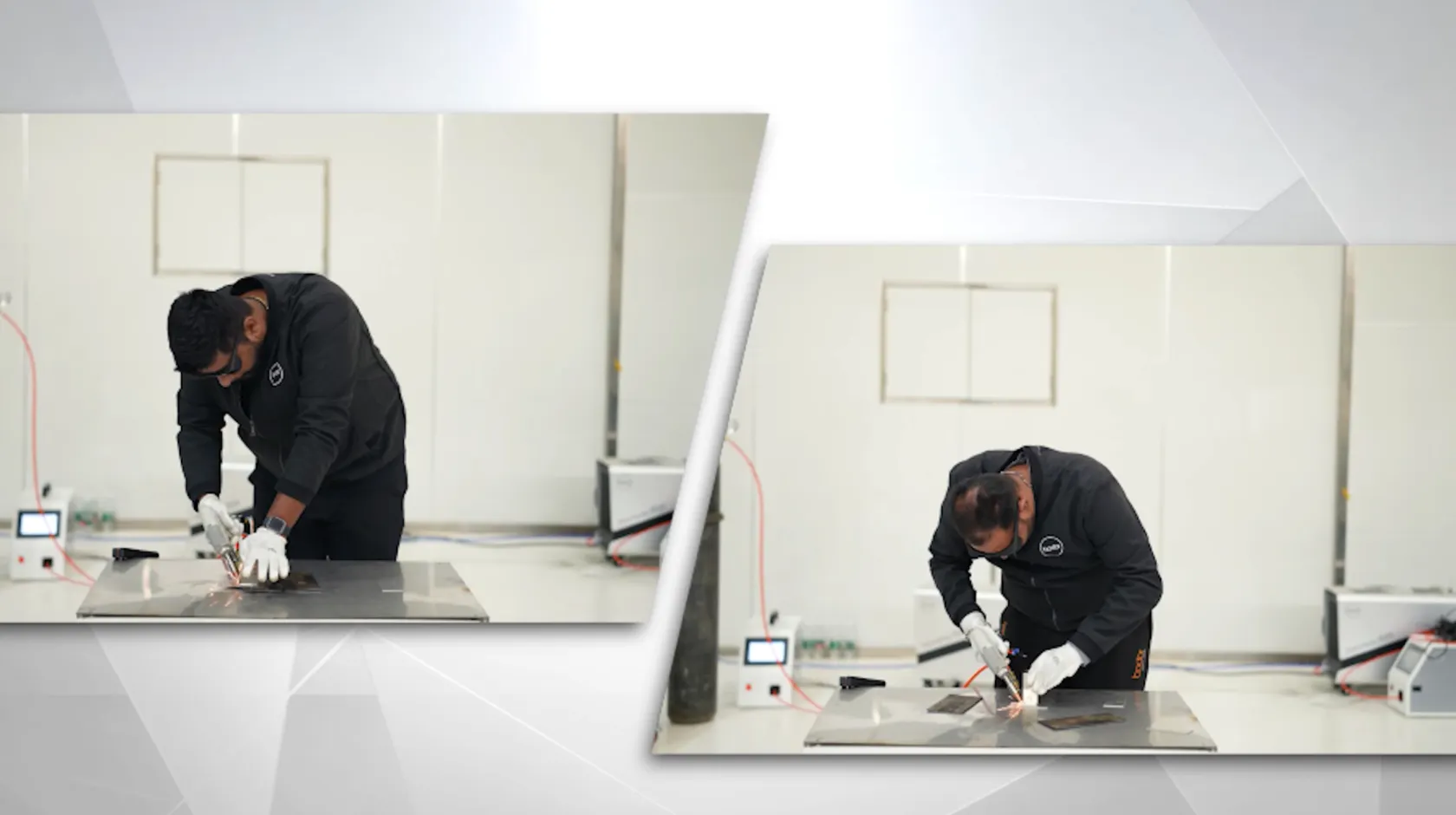
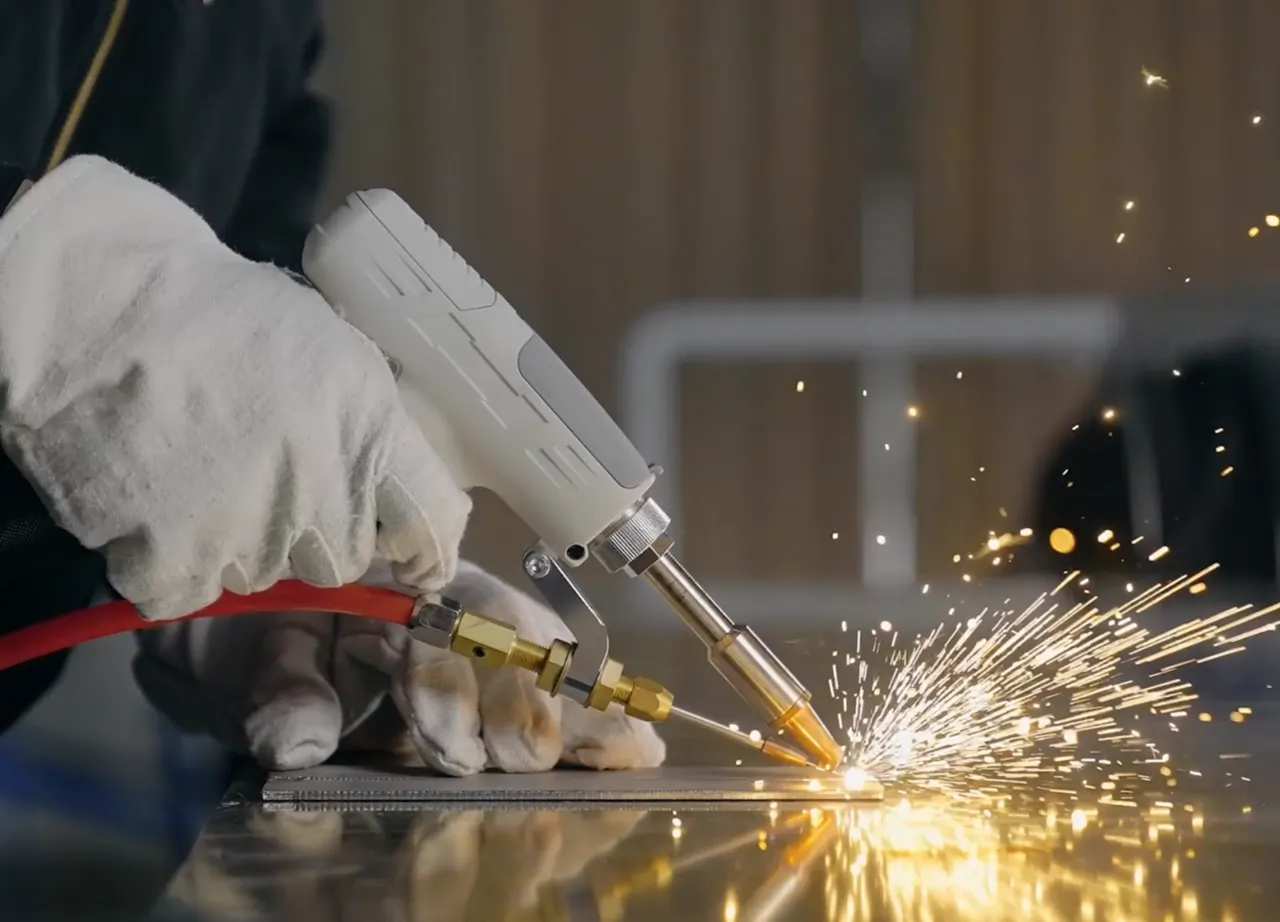
Laser welding is a technique used to join metal or thermoplastic pieces with a concentrated heat source. Since it is able to create very solid and precise weld seams, manufacturers often use it for joining delicate, heat-sensitive pieces.
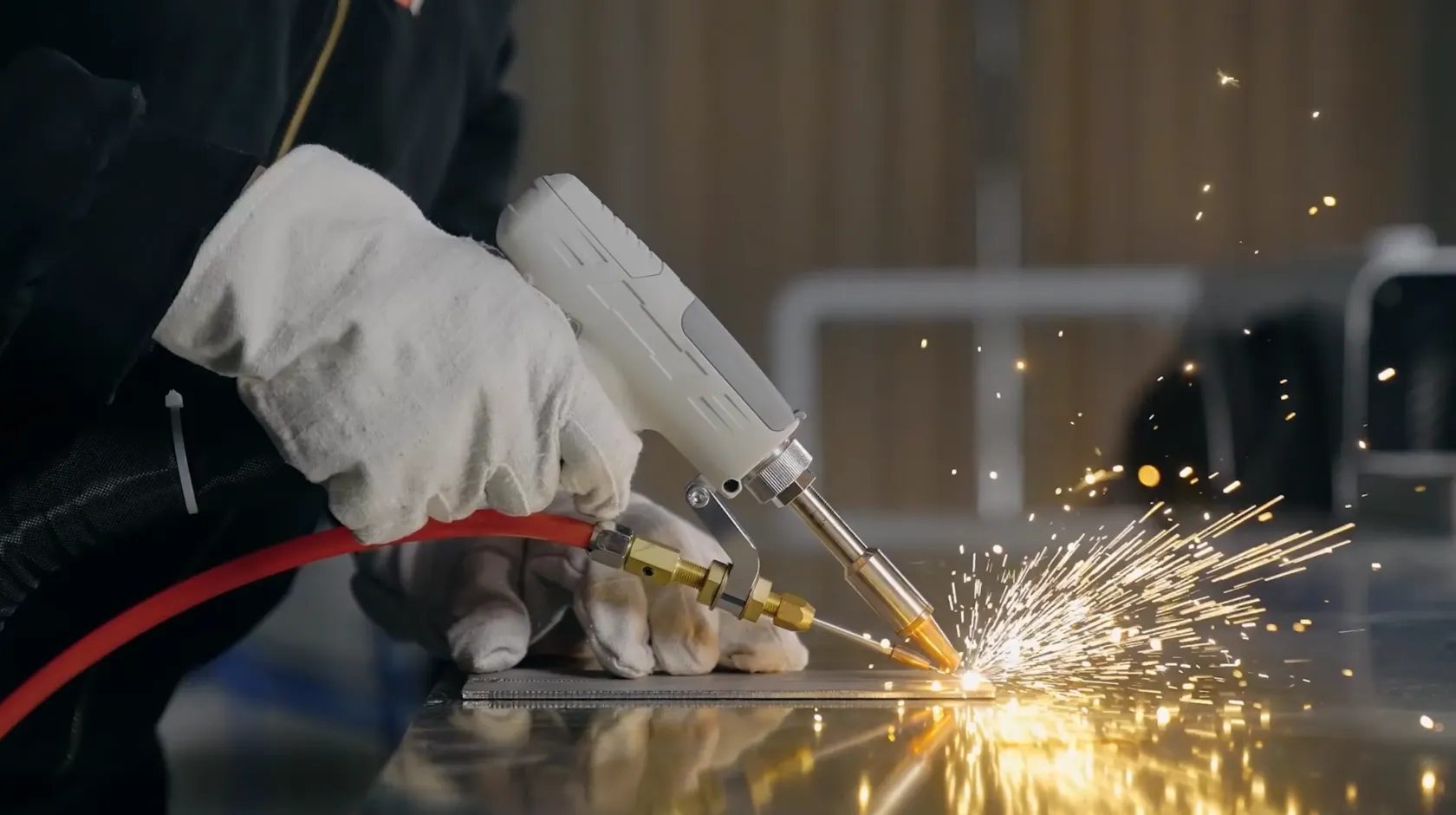

TIG welding
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, or gas metal arc welding, operates with a non-consumable tungsten electrode that delivers currents to the welding arc. The shielding gas works as a layer of protection, making sure it could consistently produce clean welds.

Differences between laser welding and TIG welding
One major difference between laser and TIG is that TIG always requires a filler substance to operate. They also vary in terms of efficiency, heat generation, material compatibility, and operation safety.
· Efficiency
In terms of welding speeds, laser welding has proven to be at least 3 to 10 times faster than TIG. The laser component is also more compact and easier to mount on a CNC controlled machine. As a result, laser welding ensures high productivity and excels in automated manufacturing processes, further improving efficiency.
· Heat generation
Laser welding produces a much lower heat input per unit length in comparison to TIG welding, meaning that laser produces little residual stress, heat, and distortion. The rationale behind this is because laser only requires a minimal amount of energy to weld materials together.
· Material compatibility
When a laser beam is directed at the seam, the metal will be melted and fused where two pieces of materials meet. Because of this capacity to generate joints, laser welding is able to provide extremely high levels of accuracy and repeatability for welders. Therefore, laser is mostly applicable to join materials that are challenging to weld, such as stainless steel and aluminum.
On the other hand, as TIG has a relatively high heat generation, it usually ends up melting plastics and thin metal pieces even before the welding process begins.
Laser welding is compatible with the following metals and their alloys.
· Carbon steel
· Stainless steel
· Brass
· Aluminum
· Operation safety
In everyday operations, TIG welding process generates intense light, heat, and fumes. TIG welders are being exposed to potential occupational hazards like glaucoma and pneumoconiosis. On the contrary, laser welding is generically safer because it produces fewer flames and smoke. A pair of safety goggles is all it needs for welders to protect themselves from low, indirect laser radiation.

Drawbacks
Every approach has trade-offs, so it’s critical to understand your focus and goals when it comes to choosing your welding solution.
TIG welding requires welders to have high levels of skill and experience. Heat distortion in welds could also make the joints more vulnerable. The costs for filler substances could be expensive, too.
Laser welding does tackle many operational issues, but its initial investment is quite high.
That being said, consultation with a professional fabricator would always be the best way to determine which welding suits your project requirements.
Is laser welding actually better?
Laser welding is a versatile technique that excels in welding efficiency, quality, and flexibility. Compared to traditional methods like TIG, laser as well applies to a wider range of materials and thicknesses. Nowadays, many manufacturers prefer to employ laser welding tools for their fabrications. If you are looking for an economical laser welder with excellent performance, make sure to check out the Pro 1500 from Bodor. This is our first welding machine launch, and we are confident that it would fulfill everything you need for your welding projects.