Bodor Tech Blog
Trending and helpful laser knowledge for your success
Why burn marks or even holes on protective laser head lenses happen frequently in your laser cutting process? 7 reasons and how to solve
The laser head lenses can actually be reused, but they are also prone to burning, cracking, or scorching. There are many reasons for these problems. How to avoid the frequent damage of the protective lenses and achieve reuse? Bordelon, a customer service engineer with rich experience in the Latin American market of Bodor, summarized 7 major reasons and solutions for the frequent burn marks or even holes on the protective lenses in laser head.
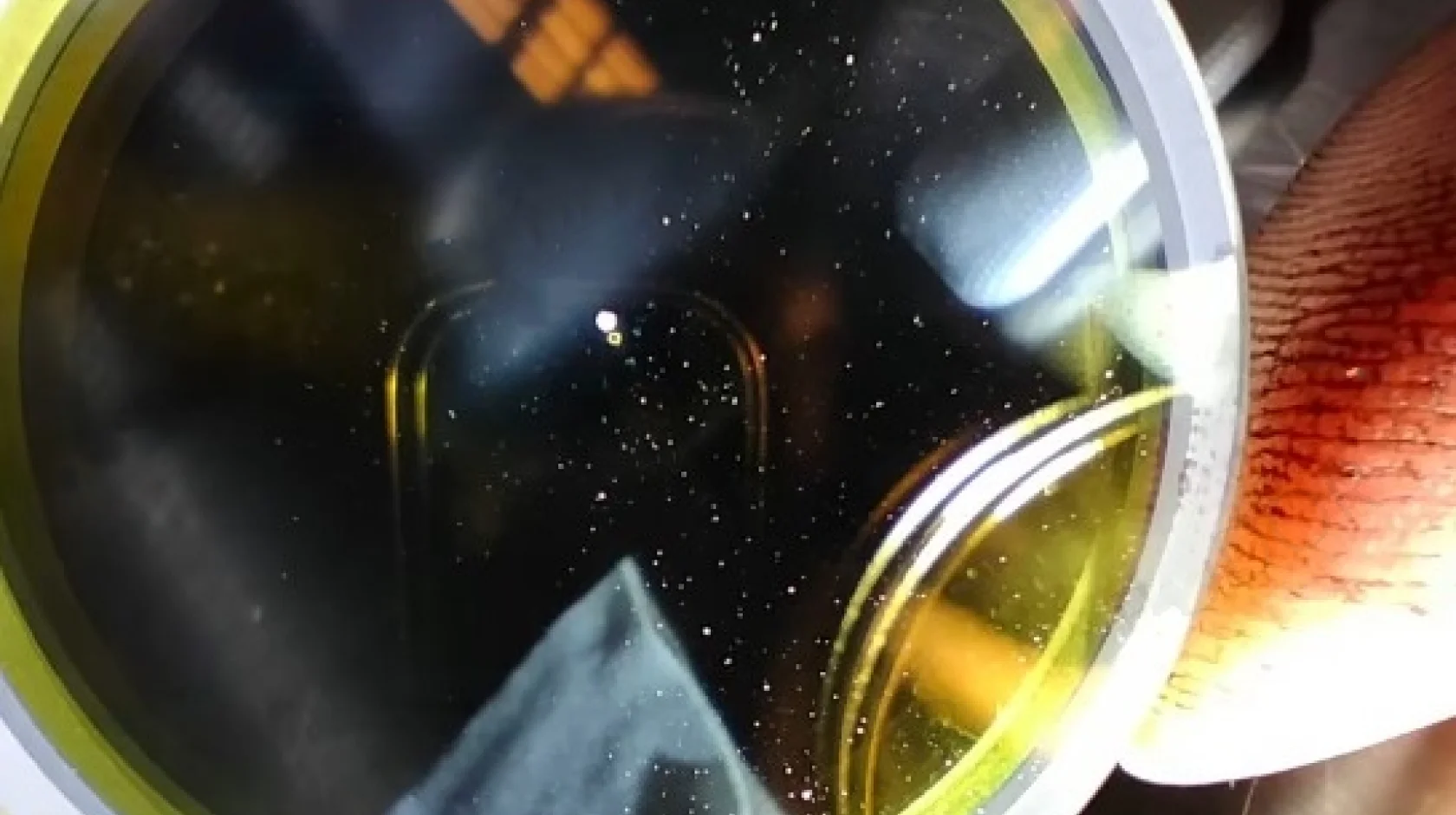
1. Negative laser focus point too low
Excessive negative focal length at the piercing point leads to the generation of back splatter onto the protective lens surface below. This is due to the drawbacks of negative focal length cutting and the unique characteristics of the piercing location. Negative focal length cutting results in increased cutting width, airflow, temperature, and piercing time, leading to the generation of a significant amount of gas, molten slag, and splatter. As the piercing point is at a certain height, a negative focal length is required, and the deeper the location, the larger the negative focal length needed. When the negative focal length is too large, there is a risk of gas, molten slag, and splatter rebounding upward, potentially contaminating the protective lens surface, affecting its transparency and heat resistance.
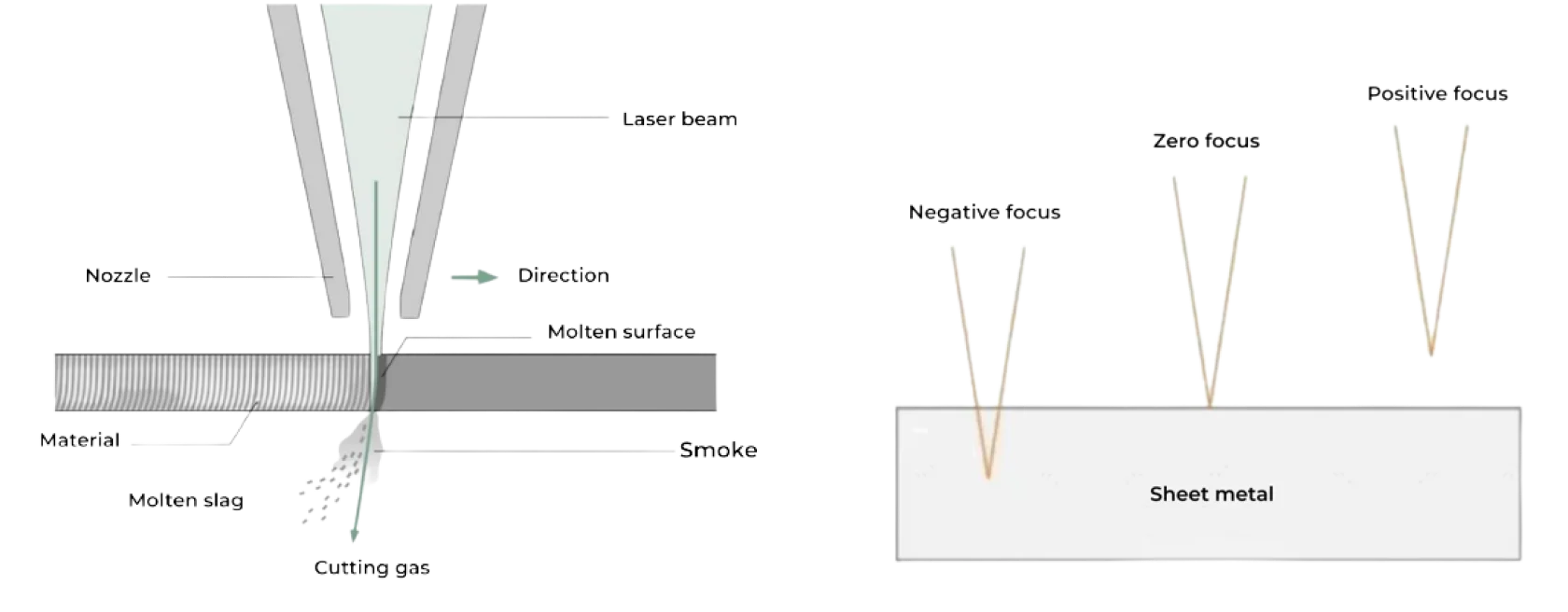
Solution: Raising the piercing focal point can improve cutting conditions and enhance piercing efficiency. Elevating the piercing focal point is equivalent to reducing the size of the negative focal length, which can reduce cutting width, airflow, temperature, and piercing time, thereby reducing the generation of gas, molten slag, and splatter. Raising the piercing focal point can also increase the spot size and energy density at the piercing location, improving piercing efficiency and quality. Furthermore, elevating the piercing focal point can reduce the likelihood of gas, molten slag, and splatter rebounding upward, protecting the protective lens surface from contamination and damage.
2. Laser precedes gas
The issue of the laser preceding the gas refers to the situation where the laser beam arrives at the workpiece surface before the auxiliary gas, leading to poor cutting results and potential damage to the protective lens or focusing lens. There are various reasons for this problem, including insufficient delay in gas blowing, resulting in the auxiliary gas not reaching the cutting position in time; insufficient or unstable auxiliary gas pressure, making it ineffective in removing slag and splatter; excessive laser power or too slow cutting speed, leading to excessive thermal impact of the laser beam on the workpiece surface.
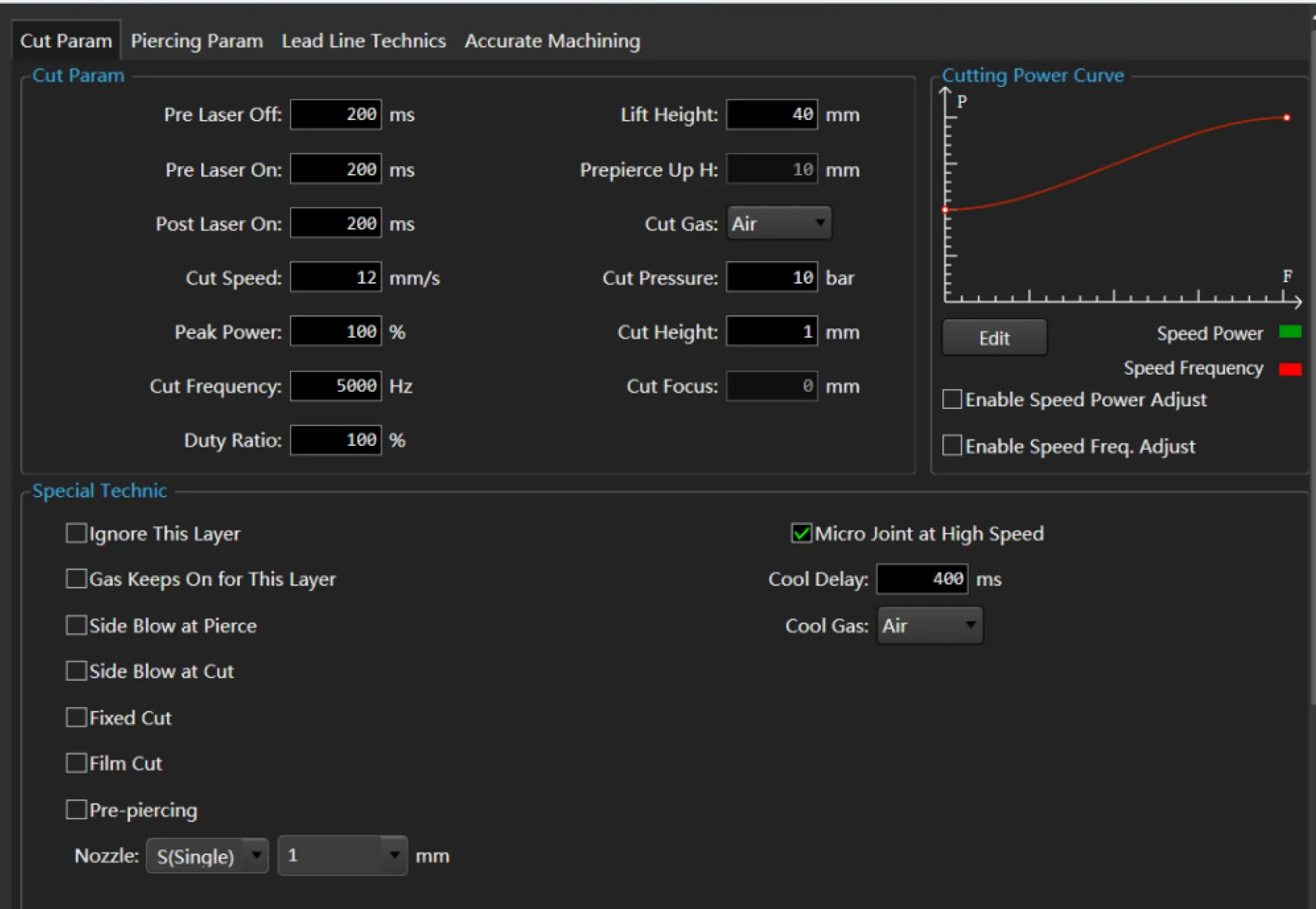
Solution: It is recommended to set the gas-on delay, first-point gas-on delay, and air change delay in the global parameters to 200-500 milliseconds. This is because the gas-on delay refers to the time interval from when the laser is turned on to when the auxiliary gas is turned on; the first-point gas-on delay refers to the time interval from the start of the first point to when the auxiliary gas is turned on; the air change delay refers to the time interval from the start of the air change to when the auxiliary gas is turned on. Setting these parameters can ensure that the auxiliary gas forms a stable airflow before the laser beam reaches the workpiece surface, thereby avoiding the laser preceding the gas issue. Additionally, attention should be paid to checking and adjusting the pressure and flow rate of the auxiliary gas, as well as the compatibility of laser power and speed.
3. Lack of piercing process
The lack of a piercing process refers to the cutting method where the plate is not pre-pierced before cutting. This approach leads to the following issues: low cutting efficiency, as there is a constant switch between cutting and piercing; poor cutting quality, as the generation of slag and splatter during cutting may contaminate the protective lens or focusing lens, affecting the quality and stability of the laser beam; high cutting costs, as the consumption of laser energy and auxiliary gas increases during cutting.
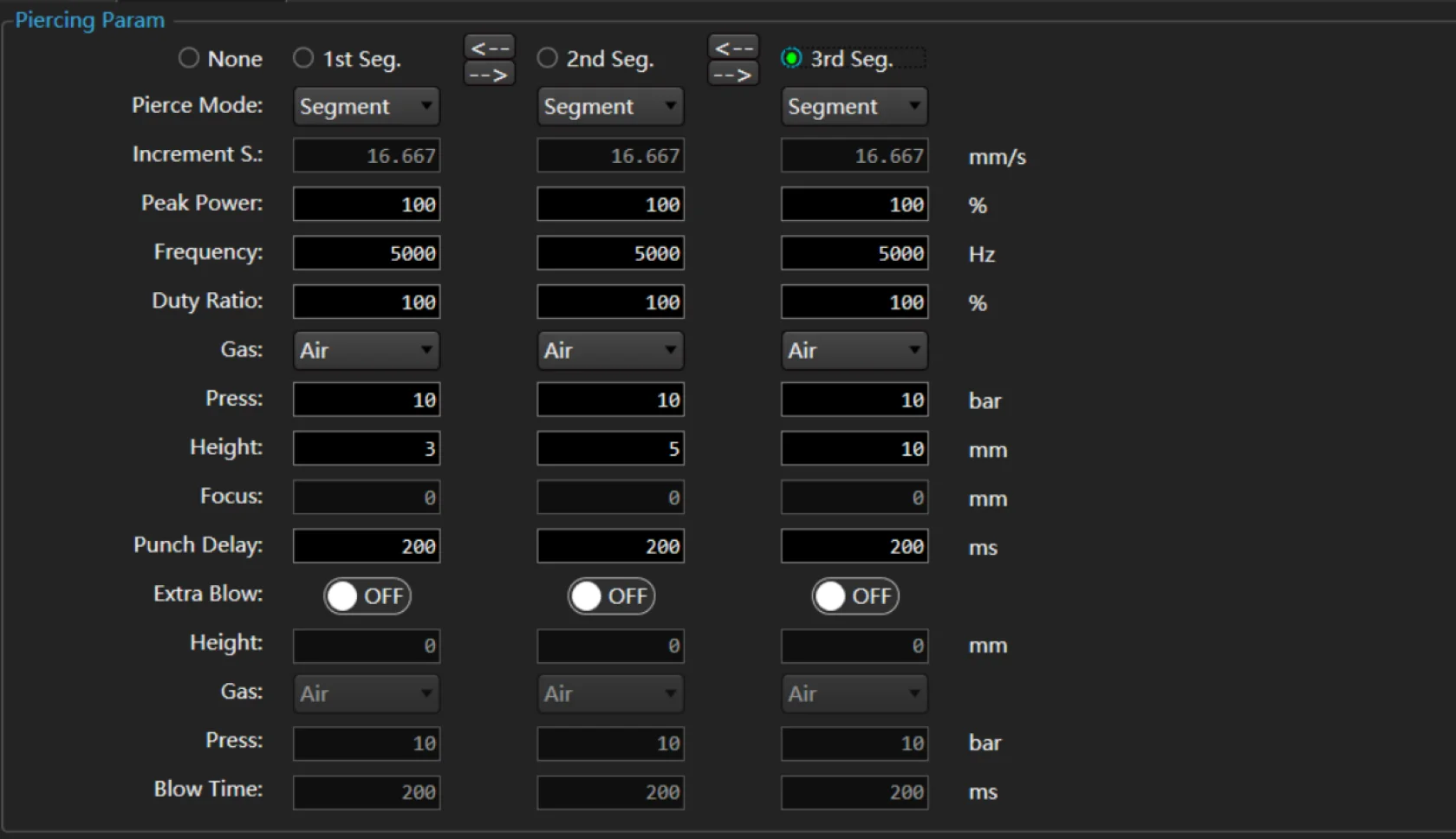
Solution: For cutting plates with a thickness of more than 1 millimeter, it is recommended to introduce a piercing process. This is because adding a piercing process can improve cutting efficiency by pre-piercing all required locations before cutting, reducing pauses and switches during the cutting process. In addition, specialized piercing parameters such as higher laser power and lower auxiliary gas pressure can be used during the piercing process to reduce the generation of slag and splatter. Adding a piercing process can also lower cutting costs by using lower laser power and higher auxiliary gas pressure during the cutting process, saving laser energy and auxiliary gas consumption.
4. Inappropriate piercing energy and time
Inappropriate piercing energy and time refer to the energy and duration of laser beam application to the plate during the piercing process. Improper piercing settings can lead to piercing blowouts, where a large hole suddenly appears on the surface of the workpiece during piercing, resulting in the following problems: low piercing efficiency, as piercing blowouts waste laser energy and auxiliary gas; poor piercing quality, as piercing blowouts can lead to surface burns, cracks, or deformation; poor piercing safety, as piercing blowouts can generate a large amount of slag and splatter, potentially harming operators or equipment.
Solution: To address this issue, reduce the duty cycle and increase the effective piercing time. The duty cycle refers to the proportion of time the laser is on in relation to the total time in pulsed laser mode. Effective piercing time refers to the actual time the laser beam interacts with the plate during the piercing process. Reducing the duty cycle can decrease the energy applied by each pulse of laser to the plate, thereby avoiding piercing blowouts. Increasing effective piercing time ensures that the laser beam provides sufficient total energy to complete the piercing process.
5. Incomplete cutting
The problem of incomplete cutting refers to the situation where the laser beam cannot completely sever the plate during the cutting process, resulting in discontinuous or uneven cutting seams. This problem may have various causes, including coaxial deviation, where the laser beam is not accurately aligned with the center position of the cutting nozzle, leading to laser beam divergence or deflection; cutting speed is too fast, exceeding the energy limit of the laser beam on the plate, making it unable to fully melt or vaporize the plate; and other factors such as plate thickness, material, surface quality, auxiliary gas type, pressure, flow rate, etc., which can also affect cutting completeness.
Solution: Depending on the specific cause, take the following measures: adjust the optical path to ensure that the laser beam is coaxial with the cutting nozzle, which can be checked and adjusted using red light or target paper. Lower the cutting speed to ensure that the laser beam has enough time and energy to cut the plate; this can be adjusted through the speed parameters on the control panel. Choose the appropriate plate thickness and material, as well as match auxiliary gas type, pressure, and flow rate, by referring to the process parameters of Bodor laser cutting machines.
6. Uneven spot distribution
The issue of uneven spot distribution refers to the laser beam's spot shape, size, and position not meeting ideal requirements after focusing, resulting in uneven energy density of the laser beam and uneven cutting effects. This problem may occur due to the poor quality of the laser beam output, subpar or contaminated optical components, or poor-quality or damaged focusing lenses.
Solution: To address this problem, you can use a red light or target paper for inspection. Red light allows for a visual assessment of the laser beam's shape and position to detect any offset or deformation. Target paper can precisely measure the energy distribution and spot size of the laser beam to detect any unevenness or excessive size. Additionally, ensure that the fiber crystal and internal components are functioning properly, and if any anomalies are found, replace or repair them promptly.
7. Poor gas quality
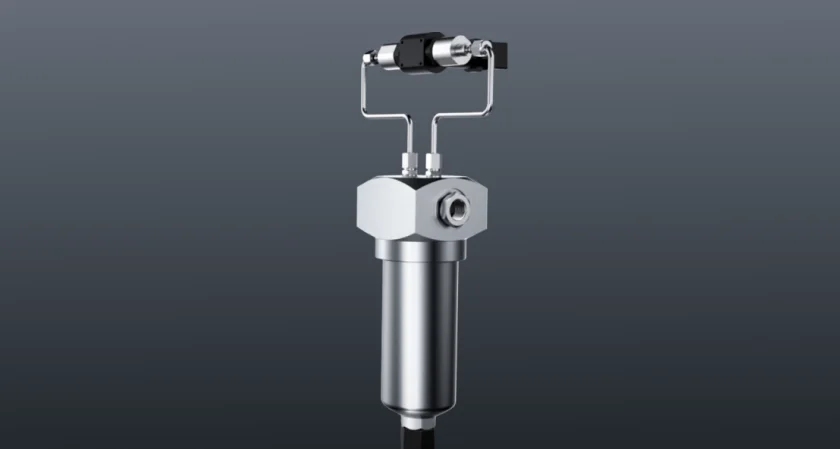
Laser cutting requires that the cutting gas does not contain moisture, dust and oil, which will directly contaminate the lens when the gas enters the laser head, thereby reducing the light transmittance and causing the lens to burn. The impurity of the gas is usually due to the customer using gas that does not meet the laser cutting requirements, or the air compressor gas cleanliness cannot meet the standard, and no vaporizer is added when using liquid nitrogen or liquid oxygen for cutting.
Solution: This problem can be solved in a targeted way. First of all, customers must use laser cutting dedicated gas; for the problem of fine dust on the lens when blowing air, Bodor’s intake filter device can be added to solve it; finally, a vaporizer is added for customers who use liquid nitrogen or liquid oxygen to prevent the gas entering the laser head from being too low in temperature and producing condensation water at the bottom of the lens.

If you want to learn more about laser cutting, please subscribe to our blog, we will update the latest content and news regularly. If you have any questions or needs, you can also contact us at any time, we will provide you with professional service and solutions as soon as possible. Thank you for your reading and support!







